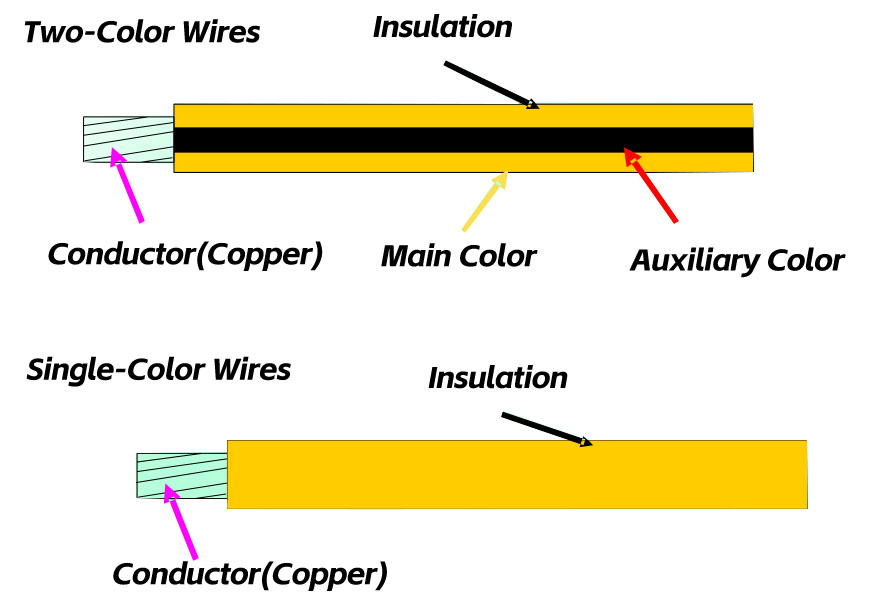
Can CCS integrated busbars replace the sampling wiring harnesses within battery modules?
The CCS integrated busbar is mainly composed of signal acquisition components, plastic structural parts, copper and aluminum bars, etc. It is connected into a whole through processes such as hot pressing or riveting. It is applied in new energy vehicles and energy storage battery modules to achieve high-voltage series and parallel connection of battery cells, as well as temperature sampling and voltage sampling of battery cells. And it transmits information such as temperature and voltage to the BMS system through the information sampling component and connector, and is part of the BMS system.
As an important electrical connection component within the battery pack/ module, different cell assembly methods, battery pack calibration parameters, usage environments, as well as requirements for the internal space and weight of the battery pack, will all have different requirements for the sampling component, production process, and material selection of the CCS integrated busbar. Therefore, to meet the diverse demands of the application end, CCS products are constantly upgrading signal acquisition components, optimizing integration processes, etc., and have developed multiple technical routes, including multiple sampling schemes such as wiring harnesses, PCBS, FPCS, FFCS, FDCS, and FCC, as well as multiple integration solutions such as injection-molded brackets, splicing, PET hot-pressed films, and vacuum-formed isolation boards.
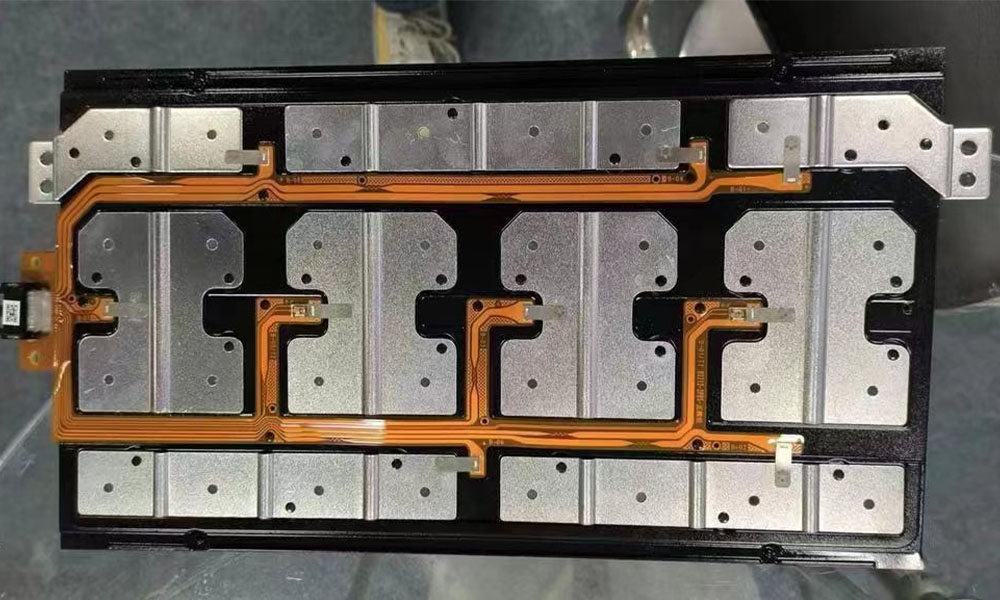

The current situation of technological development
To meet diverse application requirements, CCS products have developed multiple technical routes:
Sampling schemes: including wiring harnesses, PCBS, FPCS, FFCS, FDCS, FCC, etc
Integrated solutions: covering injection-molded brackets, splicing, PET hot-pressed films, vacuum-formed isolation boards, etc
Characteristics of mainstream integration processes:
Injection molded brackets + riveting process
Material: Flame-retardant PC+ABS or PA66
Advantages: High mechanical strength, good structural strength, and mature and stable technology
Limitations: A heavier product will affect the utilization rate of the internal space of the power battery and the improvement of its driving range. Large-sized forming is difficult, and the development of molds is challenging. The equipment cost is also high
Solution: Splicing isolation. Use several splicing support plates to replace the integrated injection molding brackets to reduce the difficulty of the injection molding process and equipment investment
Vacuum-formed isolation board + hot riveting process
Feature: Flame-retardant PC film vacuum forming
Advantages: Lightweight, low cost, high production efficiency, and high flexibility
Limitations: Relatively poor dimensional stability and relatively poor load-bearing capacity
Hot-pressed insulating film integration
Process: PET insulating film hot-pressing molding
Features: Thin, light and regular structure, high integration, higher stability, and capable of achieving automated assembly
Limitations: Large equipment investment and low production efficiency
Flat plate structure + riveting
Application: Mainly applicable to stationary energy storage
Feature: Prominent cost advantage
Limitation: Relatively weak seismic performance
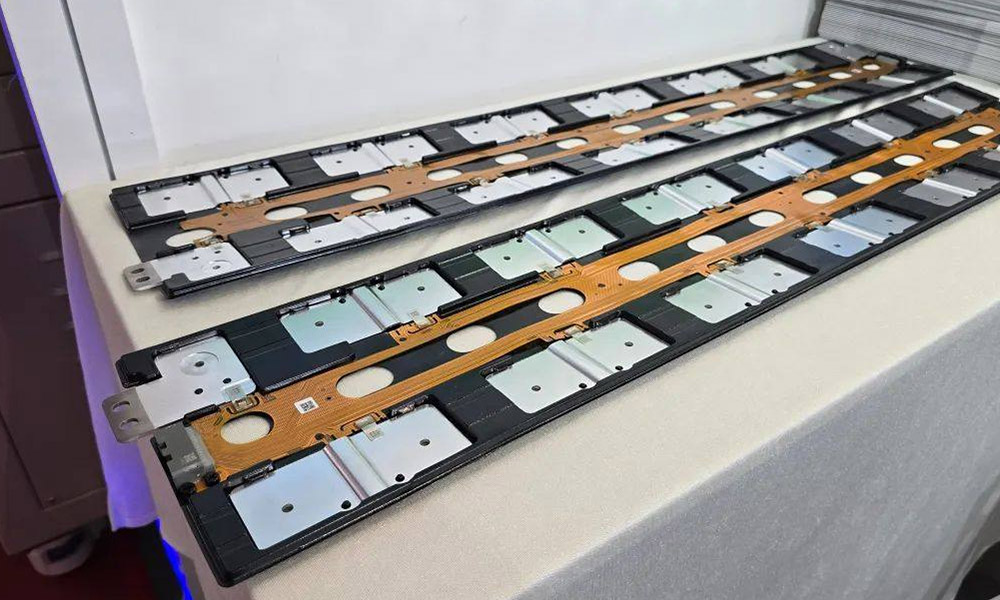
Overall, different integration processes of CCS integrated busbars each have their own advantages, and the most suitable solution should be selected based on specific application scenarios. For instance, in the field of new energy vehicles, hot-pressing or injection molding solutions can be given priority, while for fixed energy storage, flat plate riveting solutions can be selected.
Aichie is a leading provider of connection solutions in the industry, focusing on producing high-quality connectors, cables and wire harnesses. Aichie has hundreds of skilled employees in two factories, the domestic factory is located in the famous manufacturing city Dongguan City China , and the overseas factory is located in Tan Uyen City, Binh Duong Province, Vietnam. Products are widely used in industries such as Automobiles, Clean Energy, Automation manufacturing, and Smart Homes.

All products produced by Aichie comply with RoHS2.0 requirements, and some products meet environmental protection requirements such as REACH and halogen-free; Aichie has passed ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949 certifications, and is also a UL/CUL/CE recognized manufacturer.
"Quick response, exceeding expectations" is Aichie's business philosophy. Aichie has a professional engineering team, automated production equipment and a flexible production system, which can provide customers with one-stop services from product design, sample verification, production and manufacturing to packaging and shipment.
Welcome to cooperate with us,we will do our best to help you win much more business opportunities!